Spaghetti Models

Spaghetti models, also known as ensemble forecasts, are a type of weather forecasting technique that involves running multiple computer models with slightly different initial conditions. The results of these models are then combined to create a single forecast that is more accurate than any of the individual models.
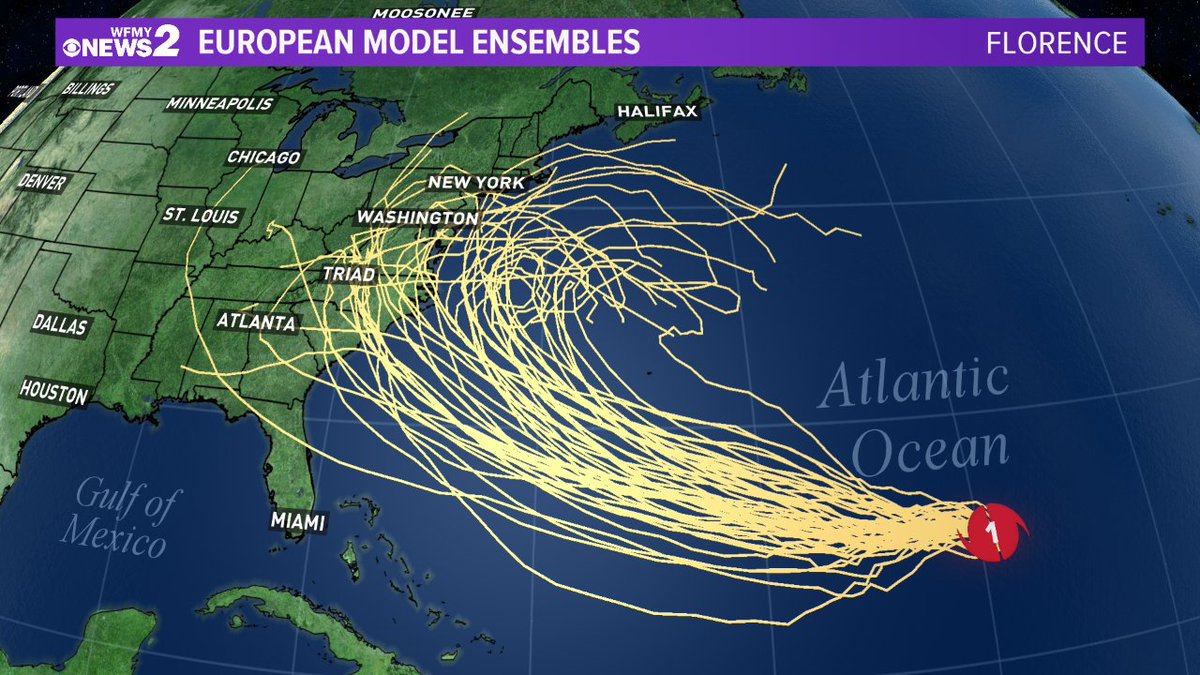
Spaghetti models show different possible paths a storm could take. Hurricane Beryl spaghetti models show the possible paths of the hurricane. Different models use different data, so they can give different results. Spaghetti models are a helpful tool for forecasters, but they are not perfect.
They can’t predict exactly where a storm will go, but they can give a general idea of the possible paths.
Types of Spaghetti Models
There are two main types of spaghetti models: deterministic and probabilistic. Deterministic models produce a single forecast, while probabilistic models produce a range of possible forecasts. Probabilistic models are more accurate than deterministic models, but they are also more difficult to interpret.
Applications of Spaghetti Models
Spaghetti models are used in a variety of industries, including weather forecasting, climate research, and finance. In weather forecasting, spaghetti models are used to predict the path of hurricanes and other storms. In climate research, spaghetti models are used to predict long-term climate trends. In finance, spaghetti models are used to predict stock prices and other financial data.
Creating and Analyzing Spaghetti Models
Creating and analyzing spaghetti models is a powerful technique for exploring complex systems and making predictions. By understanding the guidelines for creating effective models and the process of analyzing them, you can gain valuable insights into the behavior of these systems.
Creating Effective Spaghetti Models
- Define the purpose: Clearly define the goals of your model, as this will guide the data collection and analysis process.
- Collect relevant data: Gather data from reliable sources that represent the system you are studying.
- Choose appropriate variables: Select variables that are relevant to the purpose of your model and that have a strong relationship with each other.
- Create a visual representation: Plot the data on a scatter plot or other visual representation to identify patterns and relationships.
Analyzing Spaghetti Models
- Identify trends and patterns: Look for linear or nonlinear relationships, clusters, and outliers in the data.
- Develop hypotheses: Formulate hypotheses about the relationships between variables based on the patterns you observe.
- Test hypotheses: Use statistical tests or other methods to verify or reject your hypotheses.
- Draw conclusions: Based on the results of your analysis, draw conclusions about the behavior of the system and make predictions about future outcomes.
Interpreting and Presenting Results
- Explain the model: Clearly communicate the purpose, assumptions, and limitations of your model.
- Highlight key findings: Emphasize the most important patterns, relationships, and insights derived from the analysis.
- Use visual aids: Incorporate charts, graphs, and other visual aids to illustrate your findings and make them easier to understand.
- Communicate effectively: Present your results in a clear and concise manner, tailored to the audience’s level of understanding.
Applications of Spaghetti Models
Spaghetti models are widely used in forecasting and decision-making due to their ability to capture uncertainty and explore multiple scenarios. They have proven particularly valuable in fields such as finance, weather forecasting, and risk management.
Forecasting and Decision-Making
- Spaghetti models enable businesses to forecast demand, assess market trends, and make informed decisions about production, inventory, and pricing.
- In finance, they are used to model stock prices, predict interest rates, and evaluate investment strategies.
Risk Assessment and Scenario Planning
- Spaghetti models help organizations assess risks and plan for contingencies. By simulating different scenarios, they can identify potential vulnerabilities and develop mitigation strategies.
- In the insurance industry, they are used to model natural disasters and calculate insurance premiums.
Case Studies, Spaghetti models
- A study by the National Hurricane Center found that spaghetti models significantly improved the accuracy of hurricane track forecasts.
- A study by the World Bank used spaghetti models to assess the economic impact of climate change on developing countries.
Spaghetti models, wiry but not brittle, can mimic the weather’s unpredictability. A similar tale unfolds in beryl puerto rico , where the path of a storm can shift like the strands of spaghetti. Just as spaghetti models help us anticipate the weather’s whims, they serve as a reminder of the ever-changing nature of our surroundings.